聊聊iOS中的Mach-O 一 关于Mach-O Mach-O的全称为Mach Object,是OS X与iOS上的一种可执行文件格式。Mach本身指一种操作系统的微内核标准,被用于OS X与iOS系统的内核中。相信对于移动端的iOS开发者来说,对Mach-O文件一定不陌生,我们编译打包的iOS IPA文件,内部其实就有一个可执行的Mach-O文件,我们开发的framework和.a等动态库静态库中,也会包含Mach-O文件,本篇文章,我们就来详细看看Mach-O中究竟放的是什么,Mach-O的结构是怎样的。
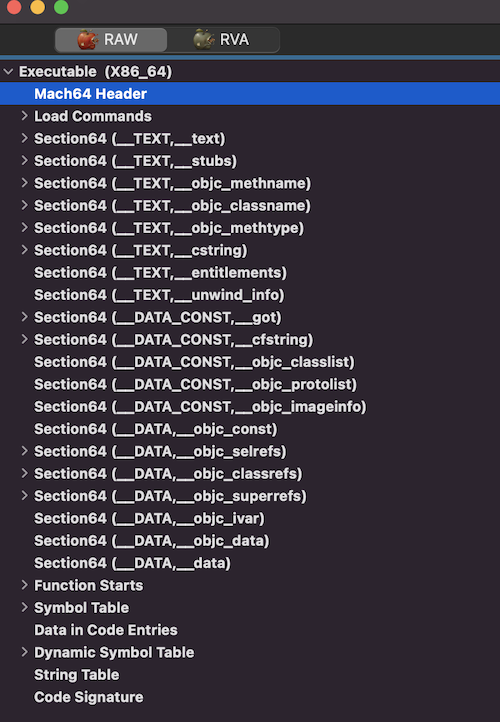
二 Mach-O头信息 Mach-O是一种文件格式,我们知道很多文件类型有包含有文件头,例如图片文件头中可能会包含图片的格式,编码方式等,压缩文件的文件头中包含压缩参数等等。相比,Mach-O是一种更加复杂的文件,其文件头中提供的信息也更多。我们可以在Github上找到一款开源的Mach-O文件阅读软件:MachOView。可以尝试用其打开任意一个编译好的IPA包中的Mach-O文件,例如:
可以看到,格式化后的文件内容中,有一项是Mach64 Header,这一项内容也是在Mach-O文件的最前部,这里就是Mach-O文件头。
关于Mach-O头部,我们可以在usr/include/mach-o/Loader.h文件中找到对应的定义,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 struct mach_header { uint32_t magic; cpu_type_t cputype; cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; uint32_t filetype; uint32_t ncmds; uint32_t sizeofcmds; uint32_t flags; }; struct mach_header_64 { uint32_t magic; cpu_type_t cputype; cpu_subtype_t cpusubtype; uint32_t filetype; uint32_t ncmds; uint32_t sizeofcmds; uint32_t flags; uint32_t reserved; };
可以看到,32位的Mach-O和64位的Mach-O最大的区别只在于64位的多了一个reserved字段,此字段当前并没有特殊意义,其预留给未来使用。下面我们来详细看下这些字段的意义。
1.magic
从其数据类型uint32_t也可以看出,magic占32个二进制位。顾名思义,这个字段是一个魔数,用来区分当前Mach-O是32位的还是64位的,有两个宏对此魔数的值进行了定义:
1 2 3 4 #define MH_MAGIC 0xfeedface #define MH_MAGIC_64 0xfeedfacf
你可以看下MachOView软件格式化后的此字段的值,是否和这些宏是对应的。
2.cputype
此字段占32个二进制位,用来描述CPU类型,相关宏定义在mach/machine.h头文件中,如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 #define CPU_TYPE_ANY ((cpu_type_t) -1) #define CPU_TYPE_VAX ((cpu_type_t) 1) #define CPU_TYPE_MC680x0 ((cpu_type_t) 6) #define CPU_TYPE_X86 ((cpu_type_t) 7) #define CPU_TYPE_I386 CPU_TYPE_X86 #define CPU_TYPE_X86_64 (CPU_TYPE_X86 | CPU_ARCH_ABI64) #define CPU_TYPE_MC98000 ((cpu_type_t) 10) #define CPU_TYPE_HPPA ((cpu_type_t) 11) #define CPU_TYPE_ARM ((cpu_type_t) 12) #define CPU_TYPE_ARM64 (CPU_TYPE_ARM | CPU_ARCH_ABI64) #define CPU_TYPE_ARM64_32 (CPU_TYPE_ARM | CPU_ARCH_ABI64_32) #define CPU_TYPE_MC88000 ((cpu_type_t) 13) #define CPU_TYPE_SPARC ((cpu_type_t) 14) #define CPU_TYPE_I860 ((cpu_type_t) 15) #define CPU_TYPE_POWERPC ((cpu_type_t) 18) #define CPU_TYPE_POWERPC64 (CPU_TYPE_POWERPC | CPU_ARCH_ABI64)
其中的cpu_type_t其实就是int类型的别名。
3.cpusubtype
CPU子类型,定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MASK 0xff000000 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_LIB64 0x80000000 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PTRAUTH_ABI 0x80000000 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ANY ((cpu_subtype_t) -1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MULTIPLE ((cpu_subtype_t) -1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_LITTLE_ENDIAN ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_BIG_ENDIAN ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX780 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX785 ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX750 ((cpu_subtype_t) 3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX730 ((cpu_subtype_t) 4) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_UVAXI ((cpu_subtype_t) 5) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_UVAXII ((cpu_subtype_t) 6) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX8200 ((cpu_subtype_t) 7) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX8500 ((cpu_subtype_t) 8) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX8600 ((cpu_subtype_t) 9) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX8650 ((cpu_subtype_t) 10) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_VAX8800 ((cpu_subtype_t) 11) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_UVAXIII ((cpu_subtype_t) 12) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC680x0_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC68030 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC68040 ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC68030_ONLY ((cpu_subtype_t) 3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(f, m) ((cpu_subtype_t) (f) + ((m) << 4)) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_I386_ALL CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(3, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_386 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(3, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_486 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(4, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_486SX CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(4, 8) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_586 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(5, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENT CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(5, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTPRO CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(6, 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTII_M3 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(6, 3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTII_M5 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(6, 5) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_CELERON CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(7, 6) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_CELERON_MOBILE CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(7, 7) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_3 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(8, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_3_M CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(8, 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_3_XEON CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(8, 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_M CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(9, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_4 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(10, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_PENTIUM_4_M CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(10, 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ITANIUM CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(11, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ITANIUM_2 CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(11, 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_XEON CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(12, 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_XEON_MP CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL(12, 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL_FAMILY(x) ((x) & 15) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL_FAMILY_MAX 15 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL_MODEL(x) ((x) >> 4) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_INTEL_MODEL_ALL 0 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_X86_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t)3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_X86_64_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t)3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_X86_ARCH1 ((cpu_subtype_t)4) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_X86_64_H ((cpu_subtype_t)8) #define CPU_THREADTYPE_INTEL_HTT ((cpu_threadtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R2300 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R2600 ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R2800 ((cpu_subtype_t) 3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R2000a ((cpu_subtype_t) 4) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R2000 ((cpu_subtype_t) 5) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R3000a ((cpu_subtype_t) 6) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MIPS_R3000 ((cpu_subtype_t) 7) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC98000_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC98601 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_HPPA_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_HPPA_7100 ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_HPPA_7100LC ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC88000_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC88100 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_MC88110 ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_SPARC_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_I860_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_I860_860 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_601 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_602 ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_603 ((cpu_subtype_t) 3) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_603e ((cpu_subtype_t) 4) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_603ev ((cpu_subtype_t) 5) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_604 ((cpu_subtype_t) 6) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_604e ((cpu_subtype_t) 7) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_620 ((cpu_subtype_t) 8) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_750 ((cpu_subtype_t) 9) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_7400 ((cpu_subtype_t) 10) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_7450 ((cpu_subtype_t) 11) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_POWERPC_970 ((cpu_subtype_t) 100) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V4T ((cpu_subtype_t) 5) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V6 ((cpu_subtype_t) 6) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V5TEJ ((cpu_subtype_t) 7) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_XSCALE ((cpu_subtype_t) 8) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7 ((cpu_subtype_t) 9) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7F ((cpu_subtype_t) 10) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7S ((cpu_subtype_t) 11) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7K ((cpu_subtype_t) 12) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V8 ((cpu_subtype_t) 13) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V6M ((cpu_subtype_t) 14) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7M ((cpu_subtype_t) 15) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V7EM ((cpu_subtype_t) 16) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM_V8M ((cpu_subtype_t) 17) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_V8 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64E ((cpu_subtype_t) 2) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_PTR_AUTH_MASK 0x0f000000 #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_PTR_AUTH_VERSION(x) (((x) & CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_PTR_AUTH_MASK) >> 24) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_32_ALL ((cpu_subtype_t) 0) #define CPU_SUBTYPE_ARM64_32_V8 ((cpu_subtype_t) 1)
4.filetype
此字段标记Mach-O文件的具体类型,例如当前Mach-O是可执行文件还是库文件等,此字段占32个二进制位,值定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 #define MH_OBJECT 0x1 #define MH_EXECUTE 0x2 #define MH_FVMLIB 0x3 #define MH_CORE 0x4 #define MH_PRELOAD 0x5 #define MH_DYLIB 0x6 #define MH_DYLINKER 0x7 #define MH_BUNDLE 0x8 #define MH_DYLIB_STUB 0x9 #define MH_DSYM 0xa #define MH_KEXT_BUNDLE 0xb #define MH_FILESET 0xc
5.ncmds
此字段描述需要加载的命令条数,与Mach-O文件中的Load Commands段中的数据对应。
6.sizeofcmds
与Mach-O文件中的Load Commands段中的数据对应,标记Load Commands段的长度。
7.flags
标志位字段,标记当前Mach-O文件的一些重要信息,这些flags是以二进制位或的关系定义的,也就是说可以同时拥有多个标记。定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 #define MH_NOUNDEFS 0x1 #define MH_INCRLINK 0x2 #define MH_DYLDLINK 0x4 #define MH_BINDATLOAD 0x8 #define MH_PREBOUND 0x10 #define MH_SPLIT_SEGS 0x20 #define MH_LAZY_INIT 0x40 #define MH_TWOLEVEL 0x80 #define MH_FORCE_FLAT 0x100 #define MH_NOMULTIDEFS 0x200 #define MH_NOFIXPREBINDING 0x400 #define MH_PREBINDABLE 0x800 #define MH_ALLMODSBOUND 0x1000 #define MH_SUBSECTIONS_VIA_SYMBOLS 0x2000 #define MH_CANONICAL 0x4000 #define MH_WEAK_DEFINES 0x8000 #define MH_BINDS_TO_WEAK 0x10000 #define MH_ALLOW_STACK_EXECUTION 0x20000 #define MH_ROOT_SAFE 0x40000 #define MH_SETUID_SAFE 0x80000 #define MH_NO_REEXPORTED_DYLIBS 0x100000 #define MH_PIE 0x200000 #define MH_DEAD_STRIPPABLE_DYLIB 0x400000 #define MH_HAS_TLV_DESCRIPTORS 0x800000 #define MH_NO_HEAP_EXECUTION 0x1000000 #define MH_APP_EXTENSION_SAFE 0x02000000 #define MH_NLIST_OUTOFSYNC_WITH_DYLDINFO 0x04000000 #define MH_SIM_SUPPORT 0x08000000 #define MH_DYLIB_IN_CACHE 0x80000000
Mach-O文件头的内容大致就只有这些,上面我们提到过,ncmds和sizeofcmds描述了加载命令的条数和加载命令的内容大小,下面我们就来看下加载命令。
三 加载命令 在Mach-O文件中,加载命令段紧跟在Mach-O头数据后面,头数据中的字段告知了我们加载命令的条数和大小,通过这两个字段来具体的进行命令的解析和执行。
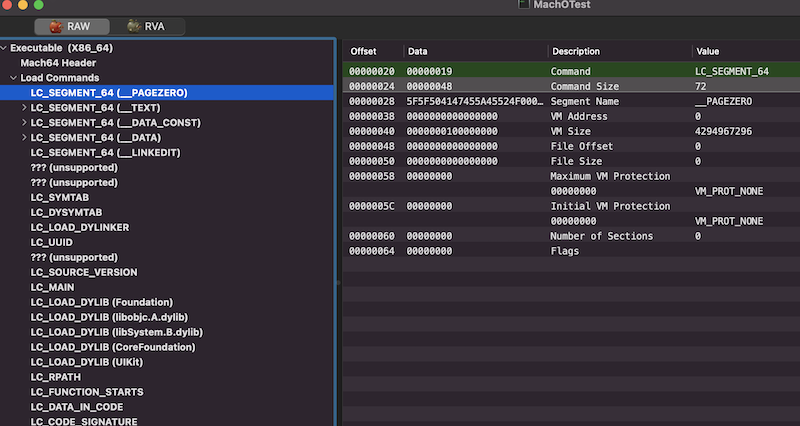
我们现在MachOView中简单浏览下这部分的数据结构,如下图:
可以看到,每条加载命令的开头结构都是一样的,即命令类型和当前命令的长度大小。其实,在loader.h头文件中有定义一个结构体来描述加载命令,如下:
1 2 3 4 struct load_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; };
可以看到,每条加载命令在解析时,首先会获取到cmd和cmdsize,cmd用来标记加载命令是什么,cmdsize指明当前加载命令的字节长度,通过这两个字段,可以对命令进行完整的解析。
下面列举了常见的命令类型,对应的宏定义:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 #define LC_SEGMENT 0x1 #define LC_SEGMENT_64 0x19 #define LC_SYMTAB 0x2 #define LC_SYMSEG 0x3 #define LC_THREAD 0x4 #define LC_UNIXTHREAD 0x5 #define LC_LOADFVMLIB 0x6 #define LC_IDFVMLIB 0x7 #define LC_IDENT 0x8 #define LC_FVMFILE 0x9 #define LC_PREPAGE 0xa #define LC_DYSYMTAB 0xb #define LC_LOAD_DYLIB 0xc #define LC_ID_DYLIB 0xd #define LC_LOAD_DYLINKER 0xe #define LC_ID_DYLINKER 0xf #define LC_PREBOUND_DYLIB 0x10 #define LC_ROUTINES 0x11 #define LC_ROUTINES_64 0x1a #define LC_SUB_FRAMEWORK 0x12 #define LC_SUB_UMBRELLA 0x13 #define LC_SUB_CLIENT 0x14 #define LC_SUB_LIBRARY 0x15 #define LC_TWOLEVEL_HINTS 0x16 #define LC_PREBIND_CKSUM 0x17 #define LC_LOAD_WEAK_DYLIB (0x18 | LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_UUID 0x1b #define LC_CODE_SIGNATURE 0x1d #define LC_SEGMENT_SPLIT_INFO 0x1e #define LC_REEXPORT_DYLIB (0x1f | LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_LAZY_LOAD_DYLIB 0x20 #define LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO 0x21 #define LC_ENCRYPTION_INFO_64 0x2C #define LC_DYLD_INFO 0x22 #define LC_DYLD_INFO_ONLY (0x22|LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_LOAD_UPWARD_DYLIB (0x23 | LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_VERSION_MIN_MACOSX 0x24 #define LC_VERSION_MIN_IPHONEOS 0x25 #define LC_VERSION_MIN_TVOS 0x2F #define LC_VERSION_MIN_WATCHOS 0x30 #define LC_FUNCTION_STARTS 0x26 #define LC_DYLD_ENVIRONMENT 0x27 #define LC_MAIN (0x28|LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_DATA_IN_CODE 0x29 #define LC_SOURCE_VERSION 0x2A #define LC_DYLIB_CODE_SIGN_DRS 0x2B #define LC_LINKER_OPTION 0x2D #define LC_LINKER_OPTIMIZATION_HINT 0x2E #define LC_NOTE 0x31 #define LC_BUILD_VERSION 0x32 #define LC_DYLD_EXPORTS_TRIE (0x33 | LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_DYLD_CHAINED_FIXUPS (0x34 | LC_REQ_DYLD) #define LC_FILESET_ENTRY (0x35 | LC_REQ_DYLD)
在加载命令段,通过解析出每条命令的类型和大小,就可以方便的获取到命令中具体的值,准确来说,一条加载命令是由类型,大小和值三部分组成的。不同类型的命令对应的值解析出来的结构也不同,下面我们来介绍几个常见的命令。
1.LC_SEGMENT/LS_SEGMENT_64
通过我们编译的iOS空项目的Mach-O文件可以看到,其中包含了很多条LS_SEGMENT_64加载命令,此命令描述了内核应该如何设置当前应用进行的内存空间,这些段将直接从Mach-O文件中对应的位置加载到内存里。LS_SEGMENT_64命令的值的结构定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 struct segment_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; char segname[16 ]; uint32_t vmaddr; uint32_t vmsize; uint32_t fileoff; uint32_t filesize; vm_prot_t maxprot; vm_prot_t initprot; uint32_t nsects; uint32_t flags; }; struct segment_command_64 { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; char segname[16 ]; uint64_t vmaddr; uint64_t vmsize; uint64_t fileoff; uint64_t filesize; vm_prot_t maxprot; vm_prot_t initprot; uint32_t nsects; uint32_t flags; };
可以看到,每个段加载命令中都提供了段的基本信息,包括名称,偏移地址,字节数,以及段有包含的分区的个数,通过此命令,进程虚拟内存的设置就变得很简单,只需要根据指令来读取信息并加载到内存即可。关于段的分析我们会在后面小节做具体的介绍。
2.LC_MAIN/LS_UNIXTHREAD
当所有库加载完成后,此命令用来进行二进制程序的主线程启动。
3.LC_CODE_SIGNATURE
Mach-O包含的数字签名,如果此签名与代码不匹配,则进程会被强制关闭。LC_CODE_SIGNATURE命令的结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 struct linkedit_data_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; uint32_t dataoff; uint32_t datasize; };
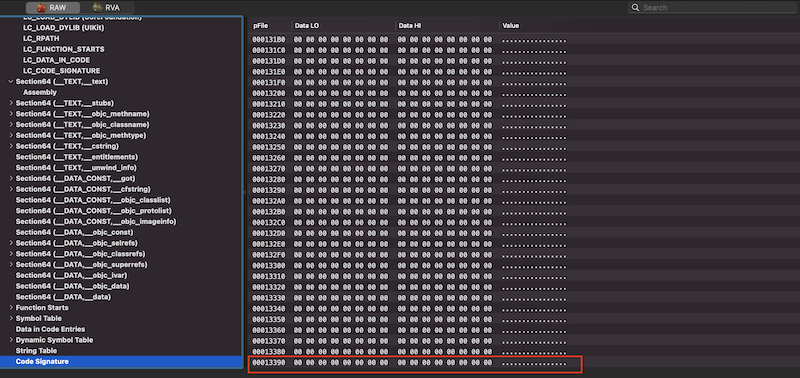
此命令的结构是一个复用的结构,很多命令都能解析成此结构,其中dataoff标记从文件的何处开始读取签名,datasize标记签名所占字节数。我们可以通过一个Mach-O文件来验证下,首先在加载命令段找到LC_CODE_SIGNATURE命令,如下:
可以看到,其offset为E8A0,size为4B00,相加后为133A0,因此我们可以得知,签名所在的位置为偏移地址为E8A0的地方,最终结束的地址为133A0,找到Code Signature段进行验证,如下:
可以看到,Code Signature段的起始偏移位置就是E8A0,最后4个字节的偏移位置为13390,再加上最后的4个字节,结尾的位置刚好为133A0,和我们计算的一致。
并非只有LC_CODE_SIGNATURE命令是采用偏移量和字节数的方式来进行加载,这种值结构的命令都是一样的逻辑,这里就不再赘述。
4.LC_SYMTAB
此命令用来加载此Mach-O文件的符号表,此命令中包含了symbol table和string table在Mach-O文件中的位置,LC_SYMTAB命令的值定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 struct symtab_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; uint32_t symoff; uint32_t nsyms; uint32_t stroff; uint32_t strsize; };
关于符号表和字符串表段,我们后面再详细介绍。
4.LC_DYSYMTAB
此命令用来加载动态库的符号表,对应的是Dynamic Symbol Table段的数据,此命令的值结构较复杂,定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 struct dysymtab_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; uint32_t ilocalsym; uint32_t nlocalsym; uint32_t iextdefsym; uint32_t nextdefsym; uint32_t iundefsym; uint32_t nundefsym; uint32_t tocoff; uint32_t ntoc; uint32_t modtaboff; uint32_t nmodtab; uint32_t extrefsymoff; uint32_t nextrefsyms; uint32_t indirectsymoff; uint32_t nindirectsyms; uint32_t extreloff; uint32_t nextrel; uint32_t locreloff; uint32_t nlocrel; };
5.LC_LOAD_DYLINKER
此命令告知内核需要调用的动态链接器的位置,值结构定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 struct dylinker_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; union lc_str name; };
6.LC_UUID
此命令加载时可以读取到一个128位的UUID值,结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 struct uuid_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; uint8_t uuid[16 ]; };
7.LC_LOAD_DYLIB
此命令用来加载额外的动态库,这也是一个非常重要的命令,最简单的iOS应用也离不开动态库的使用,通过真实的Mach-O文件我们也可以看到,通常会有多条LC_LOAD_DYLIB命令,每条命令指定一个要加载的动态库。此命令的值结构定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 struct dylib_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; struct dylib dylib ; }; struct dylib { union lc_str name; uint32_t timestamp; uint32_t current_version; uint32_t compatibility_version; };
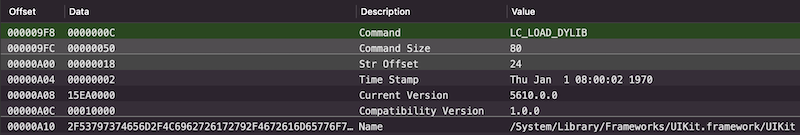
以UIKit为例,一般的iOS应用都会使用到这个动态库,此命令如下:
8.LC_RPATH
此命令用来进行@rpath外部路径变量的映射,我们知道,除了系统本身提供了一些动态共享库外,我们也可以使用外部自定义的动态库,这类外部动态库在加载的时候也需要一个明确的路径,通常在加载外部动态库的命令中,库的路径是以@rpath开头的,Xcode的编译选项中可以自定义设置外部库的寻找路径,同时使用此命令进行解析。此命令的值结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 struct rpath_command { uint32_t cmd; uint32_t cmdsize; union lc_str path; };
关于动态库这部分的内容,可以参考之前的一篇文章,其中有更详细的介绍。
https://my.oschina.net/u/2340880/blog/5323143
9.LC_FUNCTION_STARTS
此命令的结构与LC_CODE_SIGNATURE一致,用来描述函数表段所在的起始位置和字节数。关于函数表,后面会具体介绍。
四 段与分区 前面,我们将常见的加载命令进行了介绍,也有提到LS_SEGMENT是非常重要的一个命令,其指导着内核如果将Mach-O文件中的各个段数据加载到内存里。此命令的结构中有一个名为segname的字段,其表示要加载的段的名字,常用宏定义如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 #define SEG_PAGEZERO "__PAGEZERO" #define SEG_TEXT "__TEXT" #define SEG_DATA "__DATA" #define SEG_OBJC "__OBJC" #define SEG_ICON "__ICON" #define SEG_LINKEDIT "__LINKEDIT" #define SEG_UNIXSTACK "__UNIXSTACK" #define SEG_IMPORT "__IMPORT"
其中,__PAGEZERO段在进入虚拟内存时是不会分配真实的物理地址的,其只是告诉开发者此段虚拟内存不能使用,最大的作用是如果产生了空指针,会访问到此段中的地址,会直接被捕获报错。
__TEXT段为代码段,其中又包含多个区,命令中的nsects字段描述了当前段有多少个区,区的信息也在命令中进行读取,结构如下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 struct section_64 { char sectname[16 ]; char segname[16 ]; uint64_t addr; uint64_t size; uint32_t offset; uint32_t align; uint32_t reloff; uint32_t nreloc; uint32_t flags; uint32_t reserved1; uint32_t reserved2; uint32_t reserved3; };
通过这些信息可以在Mach-O文件中找到具体的分区所在的位置,将其加载进内存。
__TEXT段下,常见的区列举如下:
__text:主程序代码区
__stubs:动态链接桩区
__objc_methname:Objective-C方法名区
__objc_classname:Objective-C类名区
__objc_methtype:Objective-C方法类型区
__cstring:硬编码的C语言字符串区
__entitlements:配置文件区
__DATA_CONST段下,常见的分区列举如下:
__got:Non-Lazy Symbol Pointers区
__cfstring:程序中使用的CFStringRef区
__objc_classlist:Objective-C类列表区
__objc_protolist:Objective-C原型列表区
__objc_imginfo:Objective-C镜像信息区
__DATA段下,常见的分区列举如下:
__objc_const:Objective-C常量区
__objc_selrefs:Objective-C自引用区
__objc_classrefs:Objective-C类引用区
__objc_supperrefs:Objective-C超类引用区
五 Mach-O的”加载“到底加载的是什么 现在,我们对Mach-O文件的整体架构已经有了清晰的了解,如果将一个Mach-O文件比作一个完成的工程产品,则文件头好比是此产品的信息表,记录了产品的一些基础信息。加载命令则是产品的组装说明书,用来具体指导此工程产品的组装,之后的内容就是一个个独立的工程组件,我们只需要按照说明书的描述进行组装即可。下面我们对几个核心的区进行介绍。
1.代码段代码区 首先,对于一个iOS应用的Mach-O文件来说,__TEXT段__text分区是必不可少的,其便是程序的核心代码区,通过可视化的工具可以看到,其中数据就是汇编指令,如下:
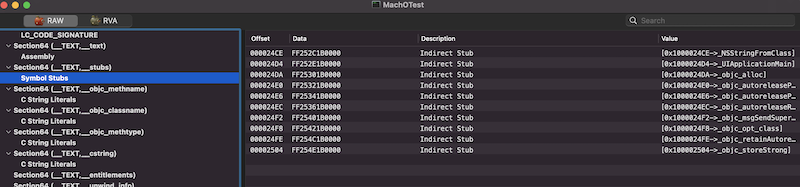
2.代码段动态链接桩区 __TEXT段__text区中的代码在调用的动态链接函数需要进行绑定,__TEXT段的__stubs区便是留的动态链接的桩,其具体的解析在Dynamic Symbol Table动态符号表段中。举个例子,__stubs区的符号解析结果如下:
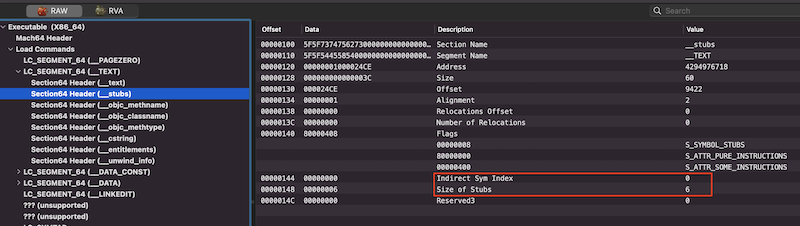
可以看到,可视化工具中,这些桩已经被解析成了具体的符号,那么是如何解析的呢。其实也很简单,首先每6个字节对应一个符号,之所以是6个字节,是LC_SEGMENT命令中的Size of Stubs字段约定的,如下:
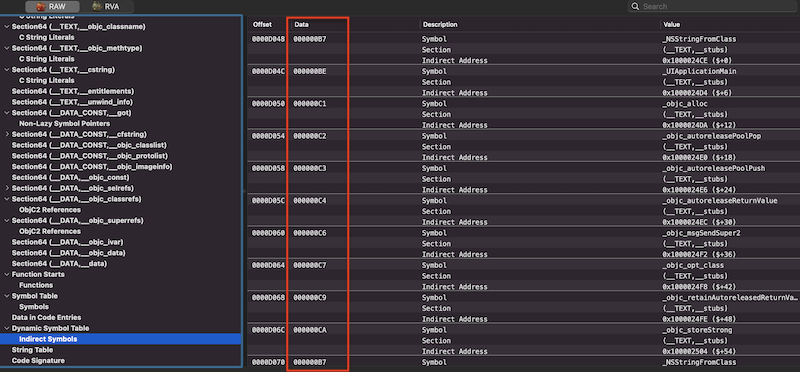
具体的符号定义在Dynamic Symbol Table里面,从前往后与__stubs中的桩一一对应,可以观察下Dynamic Symbol Table表中的数据,如下:
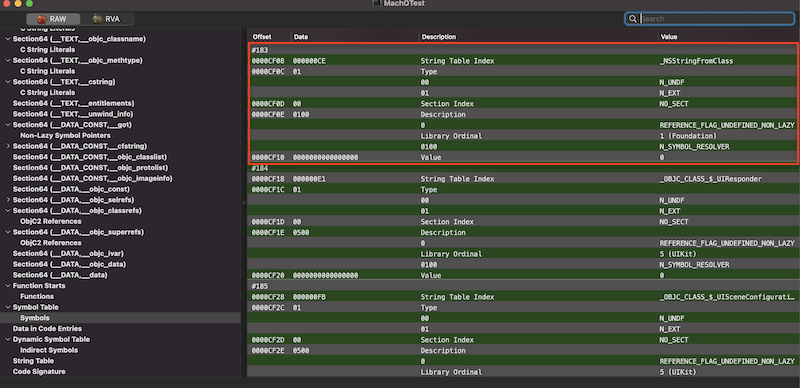
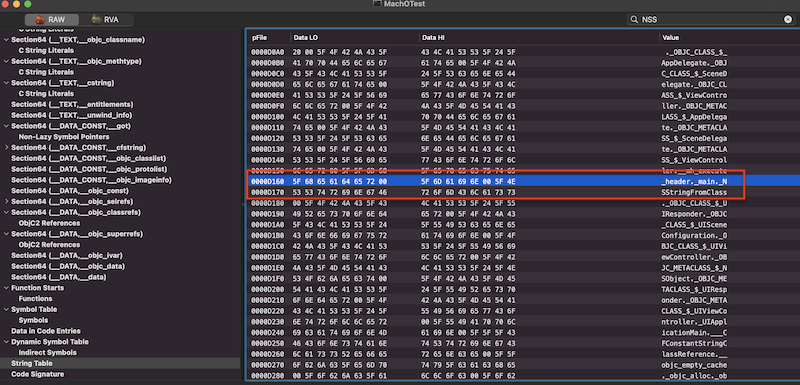
可视化工具已经帮我们将符号进行了解析,实际上动态符号表中存放的只是符号所在位置的下标,并非是符号本身,所有符号都记录在Symbol Table中,以动态符号表中的第一个符号为例,其存储的值为0xB7,转成10进制为183,表示符号表中的第183个符号,找到Symbol Table中下标为183的符号,如下:
事实上,Symbol Table中记录的是一种标准化的符号结构,其并不会存具体的符号字符串,所有字符串都存在字符串表中,以便节省内存。可以看到,Symbol Table中第183个符号记录其在字符串表中的位置为0xCE,我们在找到String Table,其起始位置为0xD0A0,加上这里的偏移量0xCE为0xD16E,说明要解析的符号存放在0xD16E的位置,String Table中记录的符号是以0x00为分割的,此处的后一个符号刚好就是_NSStringFromClass,如下:
到此,动态链接桩被解析完成。其实除了__TEXT段的__stubs区,__DATA_CONST段的__got区也是通过类似的方式来绑定符号的,只是__got区的符号需要链接时绑定,而__stubs区的符号允许运行时绑定,这里后面就不再赘述。
现在,让我们总结上符号绑定的完整过程。首先代码区中的符号需要到__stubs区或__got区进行绑定,__stubs区和__got区对应的加载命令记录了这两个去对应的符号解析的字节数以及在Dynamic Symbol Table表中的起始位置,Dynamic Symbol Table表中记录了当前符号在Symbol Table表中的下标,Symbol表记录了具体的符号实体,其中会包含当前符号在String Table中的位置,符号类型等信息,从String Table中找到具体的符号字符串。
3.Objective-C方法名区,Objective-C类名区,Objective-C方法类型区,C语言字符串区 __TEXT段的的__objc_methname区顾名思义,记录了应用中所有的Objective-C方法名,直接以字符串的方式存储。
__TEXT段的的__objc_classname区顾名思义,记录了应用中(非动态库)所有的Objective-C类名,直接以字符串的方式存储。
__TEXT段的的__objc_methtype区顾名思义,记录了应用中所有的Objective-C方法的类型,直接以字符串的方式存储。
__TEXT段的的__cstring区顾名思义,记录了应用中所有的C语言字符串,直接以字符串的方式存储。
整体看来,Mach-O文件的结构还是比较复杂的,如果没有可视化的工具,要解析此文件还是有些困难。除了MachOView工具外,我们还可以使用原生的otool命令来获取Mach-O文件中的而一些内容。文章的最后,我们来介绍几个常用的命令。
1.查看Mach-O文件头 命令:otool -h MachOTest.app/MachOTest 或 otool -hV MachOTest.app/MachOTest
hV参数的命令会自动进行可视化。
示例结果:
2.查看Mach-O的加载命令 命令:otool -lV MachOTest.app/MachOTest
示例结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 MachOTest.app/MachOTest: Load command 0 cmd LC_SEGMENT_64 cmdsize 72 segname __PAGEZERO vmaddr 0x0000000000000000 vmsize 0x0000000100000000 fileoff 0 filesize 0 maxprot --- initprot --- nsects 0 flags (none) Load command 1 cmd LC_SEGMENT_64 cmdsize 712 segname __TEXT vmaddr 0x0000000100000000 vmsize 0x0000000000004000 fileoff 0 filesize 16384 maxprot r-x initprot r-x nsects 8 flags (none) Section sectname __text segname __TEXT addr 0x0000000100001fb0 size 0x000000000000051d offset 8112 align 2^4 (16) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes PURE_INSTRUCTIONS SOME_INSTRUCTIONS reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __stubs segname __TEXT addr 0x00000001000024ce size 0x000000000000003c offset 9422 align 2^1 (2) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_SYMBOL_STUBS attributes PURE_INSTRUCTIONS SOME_INSTRUCTIONS reserved1 0 (index into indirect symbol table) reserved2 6 (size of stubs) Section sectname __objc_methname segname __TEXT addr 0x000000010000250a size 0x0000000000000dec offset 9482 align 2^0 (1) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_CSTRING_LITERALS attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_classname segname __TEXT addr 0x00000001000032f6 size 0x0000000000000070 offset 13046 align 2^0 (1) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_CSTRING_LITERALS attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_methtype segname __TEXT addr 0x0000000100003366 size 0x0000000000000b29 offset 13158 align 2^0 (1) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_CSTRING_LITERALS attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __cstring segname __TEXT addr 0x0000000100003e8f size 0x0000000000000016 offset 16015 align 2^0 (1) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_CSTRING_LITERALS attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __entitlements segname __TEXT addr 0x0000000100003ea5 size 0x000000000000010e offset 16037 align 2^0 (1) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __unwind_info segname __TEXT addr 0x0000000100003fb4 size 0x0000000000000048 offset 16308 align 2^2 (4) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Load command 2 cmd LC_SEGMENT_64 cmdsize 472 segname __DATA_CONST vmaddr 0x0000000100004000 vmsize 0x0000000000004000 fileoff 16384 filesize 16384 maxprot rw- initprot rw- nsects 5 flags SG_READ_ONLY Section sectname __got segname __DATA_CONST addr 0x0000000100004000 size 0x0000000000000060 offset 16384 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_NON_LAZY_SYMBOL_POINTERS attributes (none) reserved1 10 (index into indirect symbol table) reserved2 0 Section sectname __cfstring segname __DATA_CONST addr 0x0000000100004060 size 0x0000000000000020 offset 16480 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_classlist segname __DATA_CONST addr 0x0000000100004080 size 0x0000000000000018 offset 16512 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes NO_DEAD_STRIP reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_protolist segname __DATA_CONST addr 0x0000000100004098 size 0x0000000000000020 offset 16536 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_imageinfo segname __DATA_CONST addr 0x00000001000040b8 size 0x0000000000000008 offset 16568 align 2^2 (4) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Load command 3 cmd LC_SEGMENT_64 cmdsize 632 segname __DATA vmaddr 0x0000000100008000 vmsize 0x0000000000004000 fileoff 32768 filesize 16384 maxprot rw- initprot rw- nsects 7 flags (none) Section sectname __objc_const segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100008000 size 0x0000000000001368 offset 32768 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_selrefs segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100009368 size 0x0000000000000018 offset 37736 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_LITERAL_POINTERS attributes NO_DEAD_STRIP reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_classrefs segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100009380 size 0x0000000000000010 offset 37760 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes NO_DEAD_STRIP reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_superrefs segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100009390 size 0x0000000000000008 offset 37776 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes NO_DEAD_STRIP reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_ivar segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100009398 size 0x0000000000000008 offset 37784 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __objc_data segname __DATA addr 0x00000001000093a0 size 0x00000000000000f0 offset 37792 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Section sectname __data segname __DATA addr 0x0000000100009490 size 0x0000000000000180 offset 38032 align 2^3 (8) reloff 0 nreloc 0 type S_REGULAR attributes (none) reserved1 0 reserved2 0 Load command 4 cmd LC_SEGMENT_64 cmdsize 72 segname __LINKEDIT vmaddr 0x000000010000c000 vmsize 0x0000000000008000 fileoff 49152 filesize 29600 maxprot r-- initprot r-- nsects 0 flags (none) Load command 5 cmd LC_DYLD_CHAINED_FIXUPS cmdsize 16 dataoff 49152 datasize 680 Load command 6 cmd LC_DYLD_EXPORTS_TRIE cmdsize 16 dataoff 49832 datasize 216 Load command 7 cmd LC_SYMTAB cmdsize 24 symoff 50072 nsyms 203 stroff 53408 strsize 6144 Load command 8 cmd LC_DYSYMTAB cmdsize 80 ilocalsym 0 nlocalsym 175 iextdefsym 175 nextdefsym 8 iundefsym 183 nundefsym 20 tocoff 0 ntoc 0 modtaboff 0 nmodtab 0 extrefsymoff 0 nextrefsyms 0 indirectsymoff 53320 nindirectsyms 22 extreloff 0 nextrel 0 locreloff 0 nlocrel 0 Load command 9 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLINKER cmdsize 32 name /usr/lib/dyld (offset 12) Load command 10 cmd LC_UUID cmdsize 24 uuid 05EC375B-F3C2-3C5A-99D2-28FB938FF144 Load command 11 cmd LC_BUILD_VERSION cmdsize 32 platform IOSSIMULATOR minos 15.5 sdk 15.5 ntools 1 tool LD version 764.0 Load command 12 cmd LC_SOURCE_VERSION cmdsize 16 version 0.0 Load command 13 cmd LC_MAIN cmdsize 24 entryoff 8672 stacksize 0 Load command 14 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLIB cmdsize 88 name /System/Library/Frameworks/Foundation.framework/Foundation (offset 24) time stamp 2 Thu Jan 1 08:00:02 1970 current version 1860.0.0 compatibility version 300.0.0 Load command 15 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLIB cmdsize 56 name /usr/lib/libobjc.A.dylib (offset 24) time stamp 2 Thu Jan 1 08:00:02 1970 current version 228.0.0 compatibility version 1.0.0 Load command 16 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLIB cmdsize 56 name /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (offset 24) time stamp 2 Thu Jan 1 08:00:02 1970 current version 1311.120.1 compatibility version 1.0.0 Load command 17 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLIB cmdsize 96 name /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/CoreFoundation (offset 24) time stamp 2 Thu Jan 1 08:00:02 1970 current version 1860.0.0 compatibility version 150.0.0 Load command 18 cmd LC_LOAD_DYLIB cmdsize 80 name /System/Library/Frameworks/UIKit.framework/UIKit (offset 24) time stamp 2 Thu Jan 1 08:00:02 1970 current version 5610.0.0 compatibility version 1.0.0 Load command 19 cmd LC_RPATH cmdsize 40 path @executable_path/Frameworks (offset 12) Load command 20 cmd LC_FUNCTION_STARTS cmdsize 16 dataoff 50048 datasize 24 Load command 21 cmd LC_DATA_IN_CODE cmdsize 16 dataoff 50072 datasize 0 Load command 22 cmd LC_CODE_SIGNATURE cmdsize 16 dataoff 59552 datasize 19200
3.查看依赖的动态库 命令:otool -L MachOTest.app/MachOTest
示例结果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 MachOTest.app/MachOTest: /System/Library/Frameworks/Foundation.framework/Foundation (compatibility version 300.0.0, current version 1860.0.0) /usr/lib/libobjc.A.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 228.0.0) /usr/lib/libSystem.B.dylib (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 1311.120.1) /System/Library/Frameworks/CoreFoundation.framework/CoreFoundation (compatibility version 150.0.0, current version 1860.0.0) /System/Library/Frameworks/UIKit.framework/UIKit (compatibility version 1.0.0, current version 5610.0.0)
专注技术,懂的热爱,愿意分享,做个朋友
QQ:316045346